
PhotoFix®
DECELLULARIZED BOVINE PERICARDIUM
Feel the Difference.
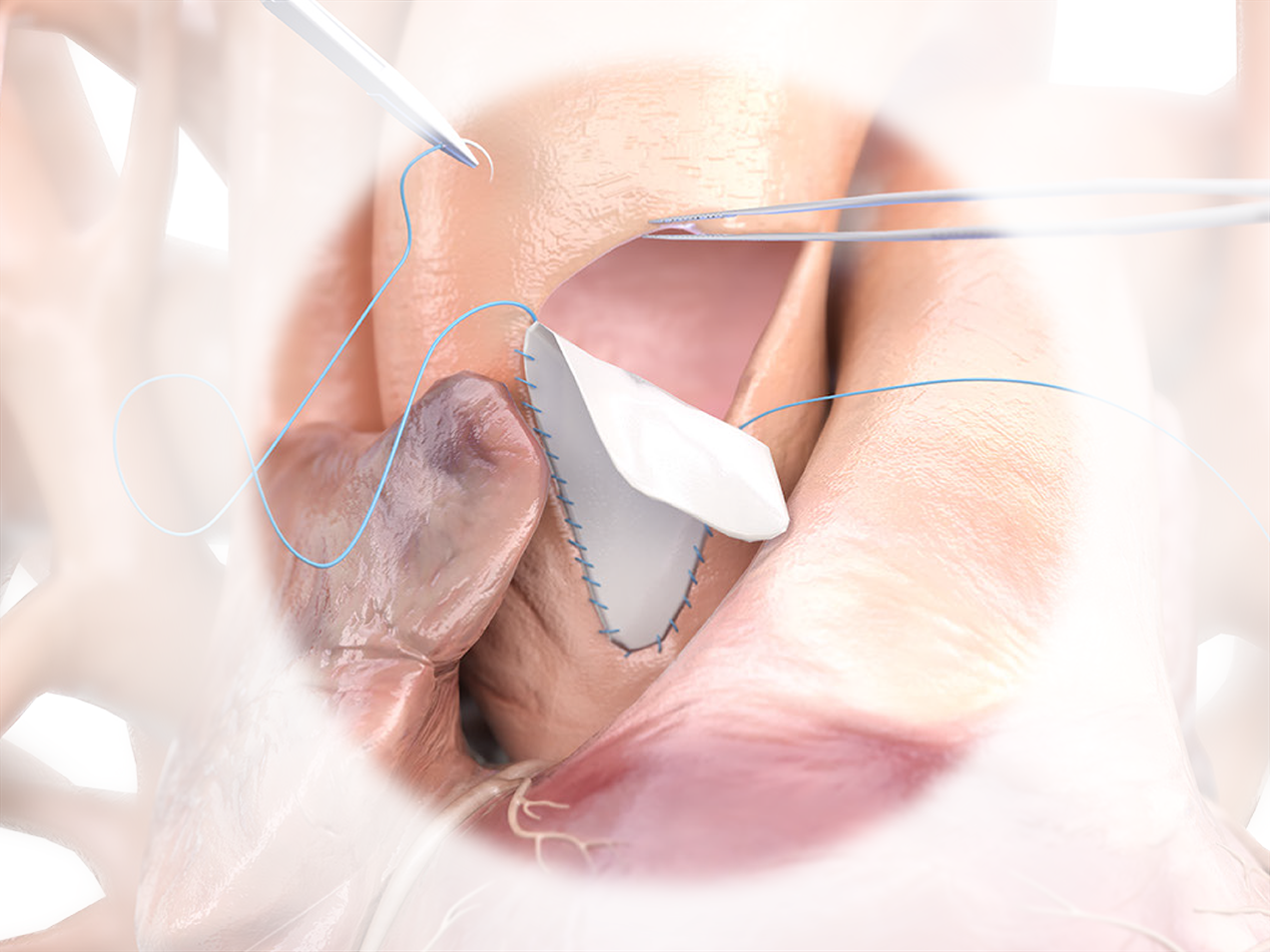
Product Highlights
- No aldehyde chemistry used in any part of the process.1
- Nonimmunogenic, biocompatible, non-cytotoxic, and maintains natural physical properties and biomechanical integrity.2
- Feels similar to autologous tissue, and is easy to trim, shape, and suture.1
Product Overview
1. NO ALDEHYDE CHEMISTRY
PhotoFix uses dye-mediated photo-oxidization to crosslink and stabilize the internal collagen structure – eliminating toxic by-products that create sites where calcium can bind to tissue.1-4
2. FEEL THE DIFFERENCE
Feels similar to Autologous tissue and is easy to trim and shape.
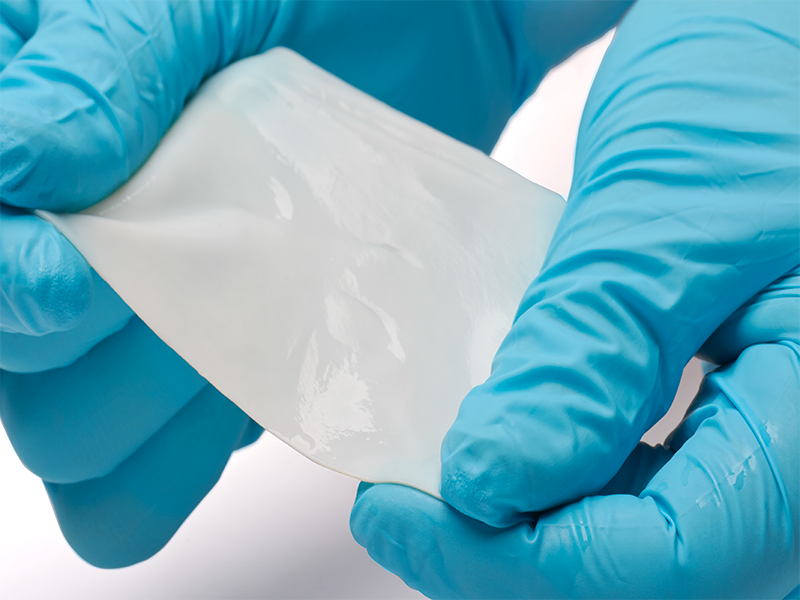

3. RELIABLE STRENGTH
Strong, uniform, and easy to suture.
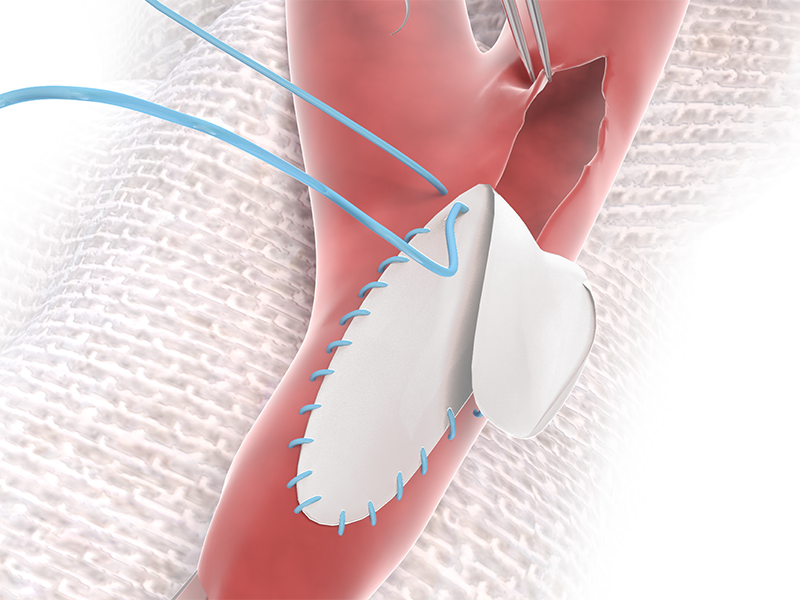
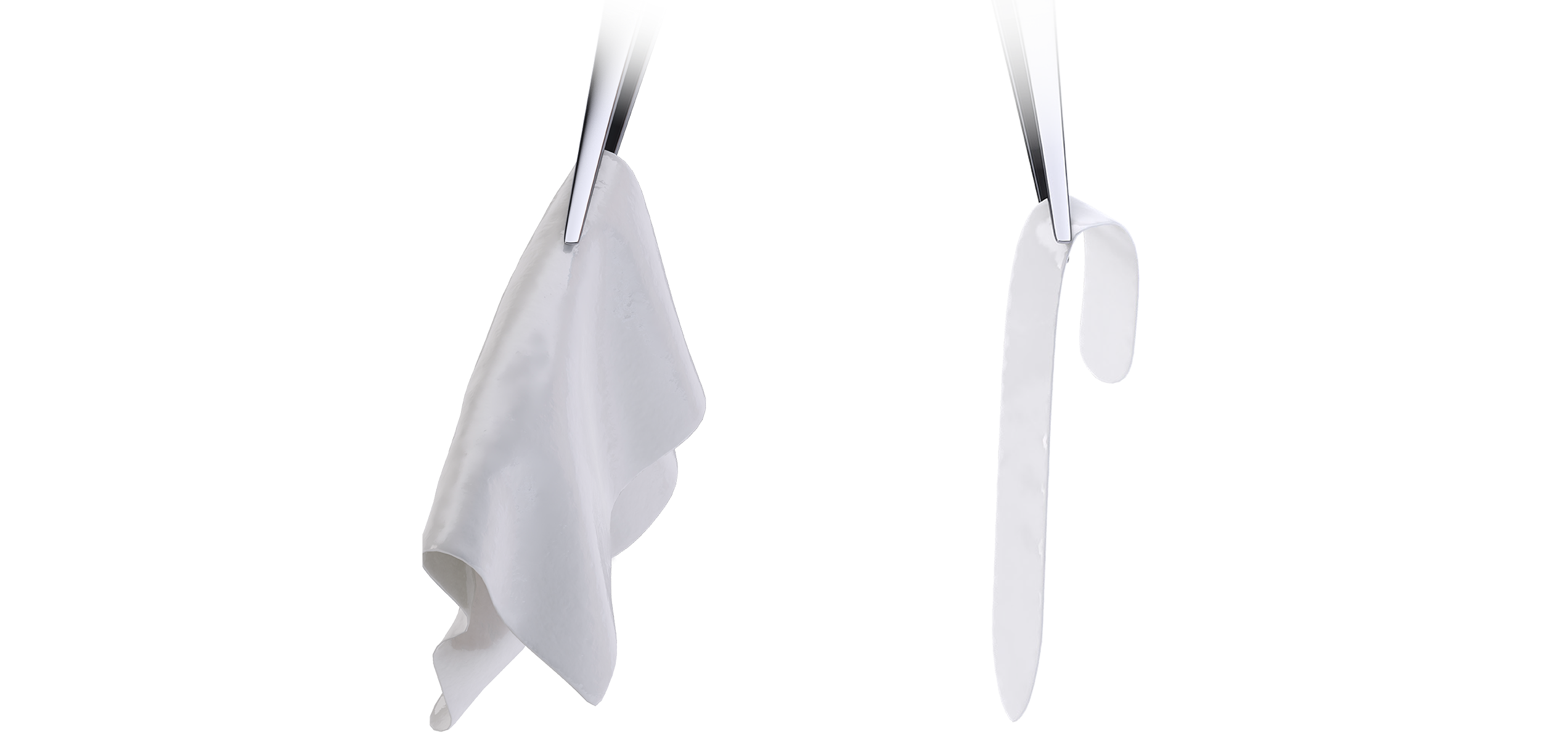
4. READY TO USE
NO Rinsing, NO Rehydrating, and
NO Waiting.


Clinical Evidence
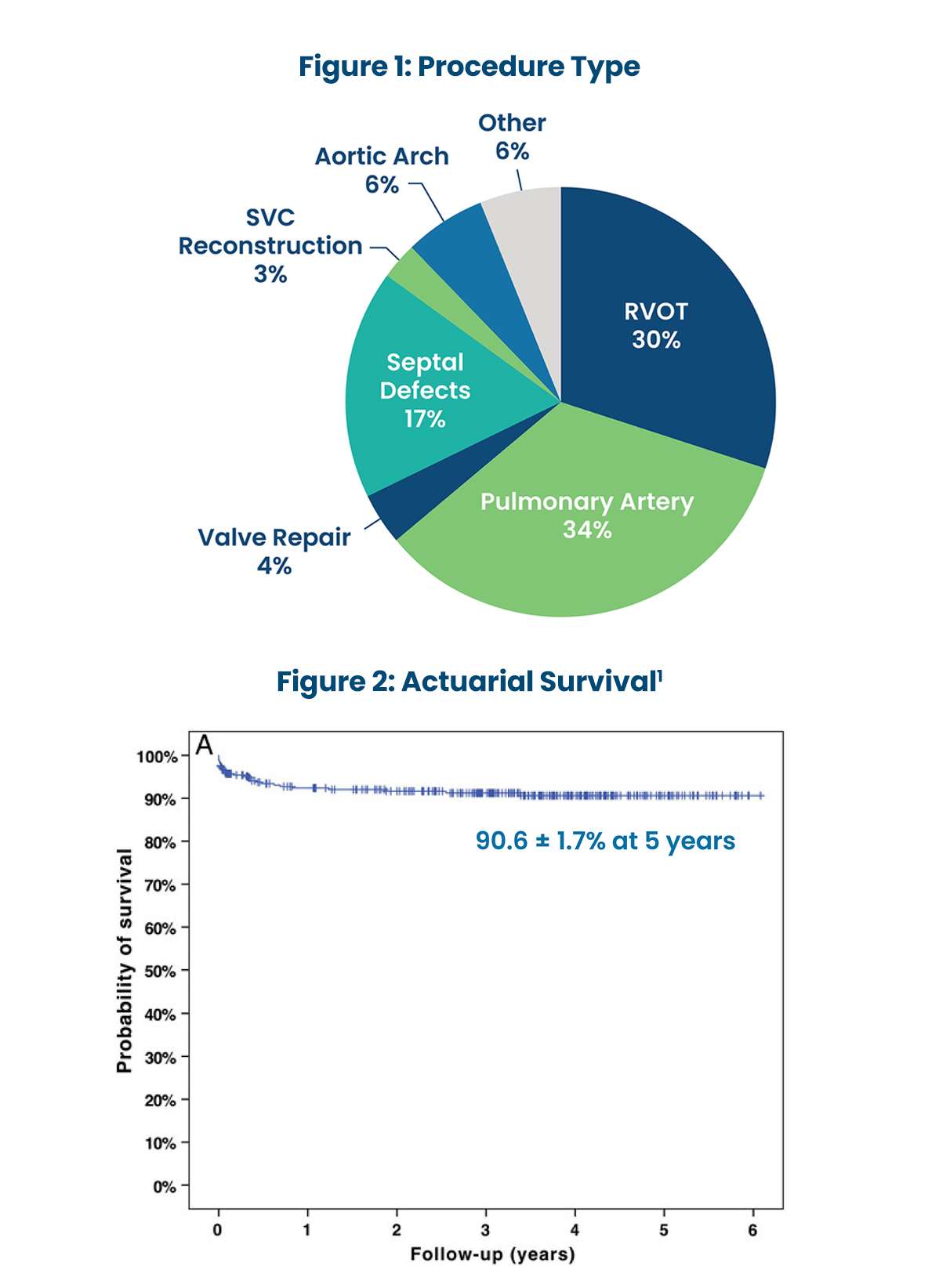
USE OF PHOTOFIX IN CONGENITAL CARDIAC SURGERY AT BOSTON CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL1
- 490 patches used between 2008 and 2011 in 364 patients (median age 5.3 years).
- Mean late follow-up of 3.2±1.6 years.
- Demonstrated excellent performance in cardiovascular repair in children.
- Wide range of applications show consistent handling characteristics and biocompatibility.
- Eight patch specimens were available for histological analysis (up to 72 months):
- “Inflammation was absent or minimal in 6 cases and mild in 2 others.”1
- “No calcification noted in 5 cases, mild calcification in 2 cases and at least moderate calcification in 1 case.”1
ANIMAL STUDIES HAVE SHOWN:
- There was no evidence of collagen degradation, thrombogenicity, infection, excessive inflammation or intrinsic calcification in sheep animal models (140 days).2
- PhotoFix process has demonstrated no significant calcification in both subcutaneous rat (60 days) implants and juvenile sheep (140 days) animal models.2
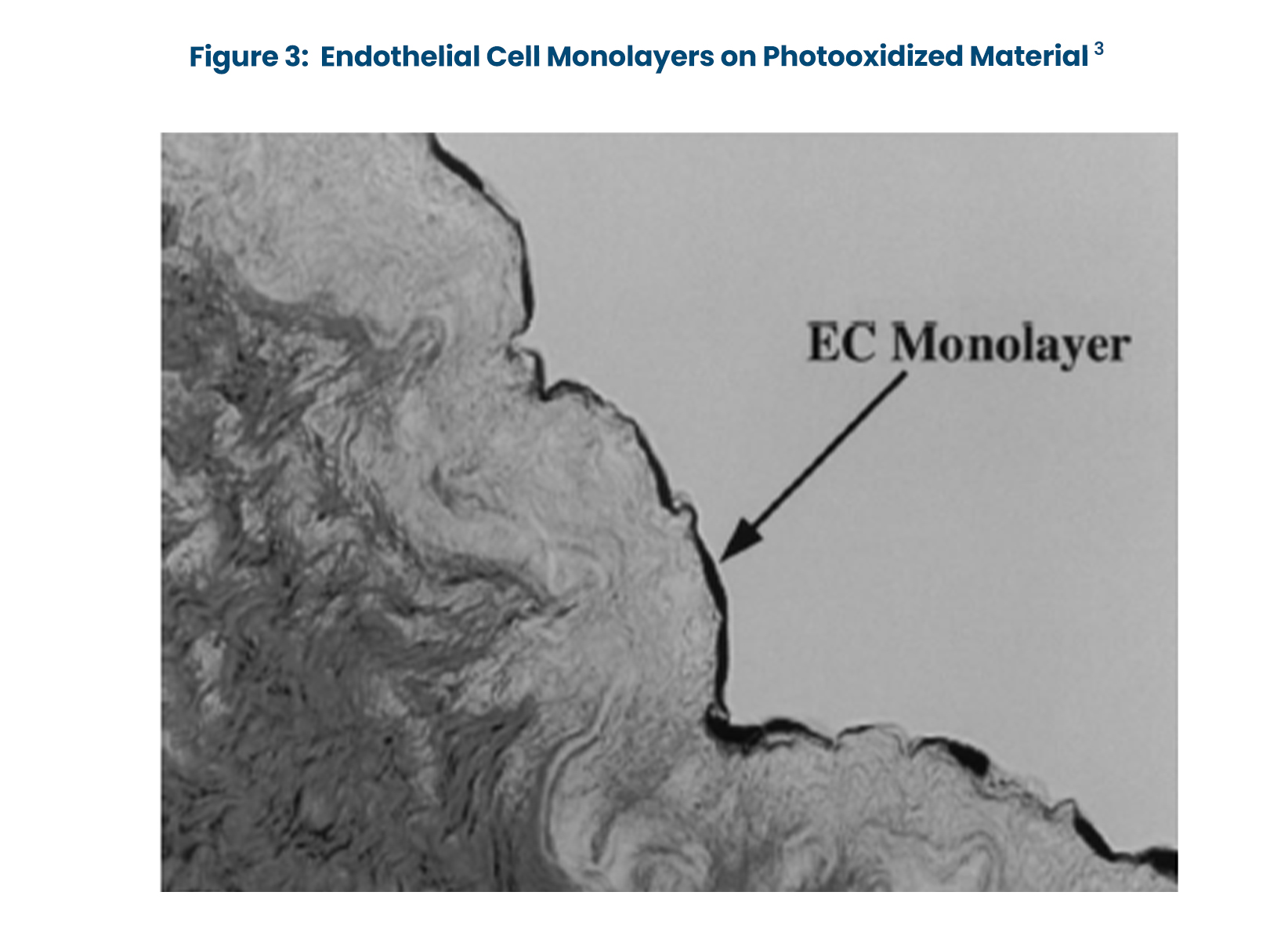
- Endothelial cell growth is supported in vitro by photooxidized pericardium and vascular grafts (Figure 3).3
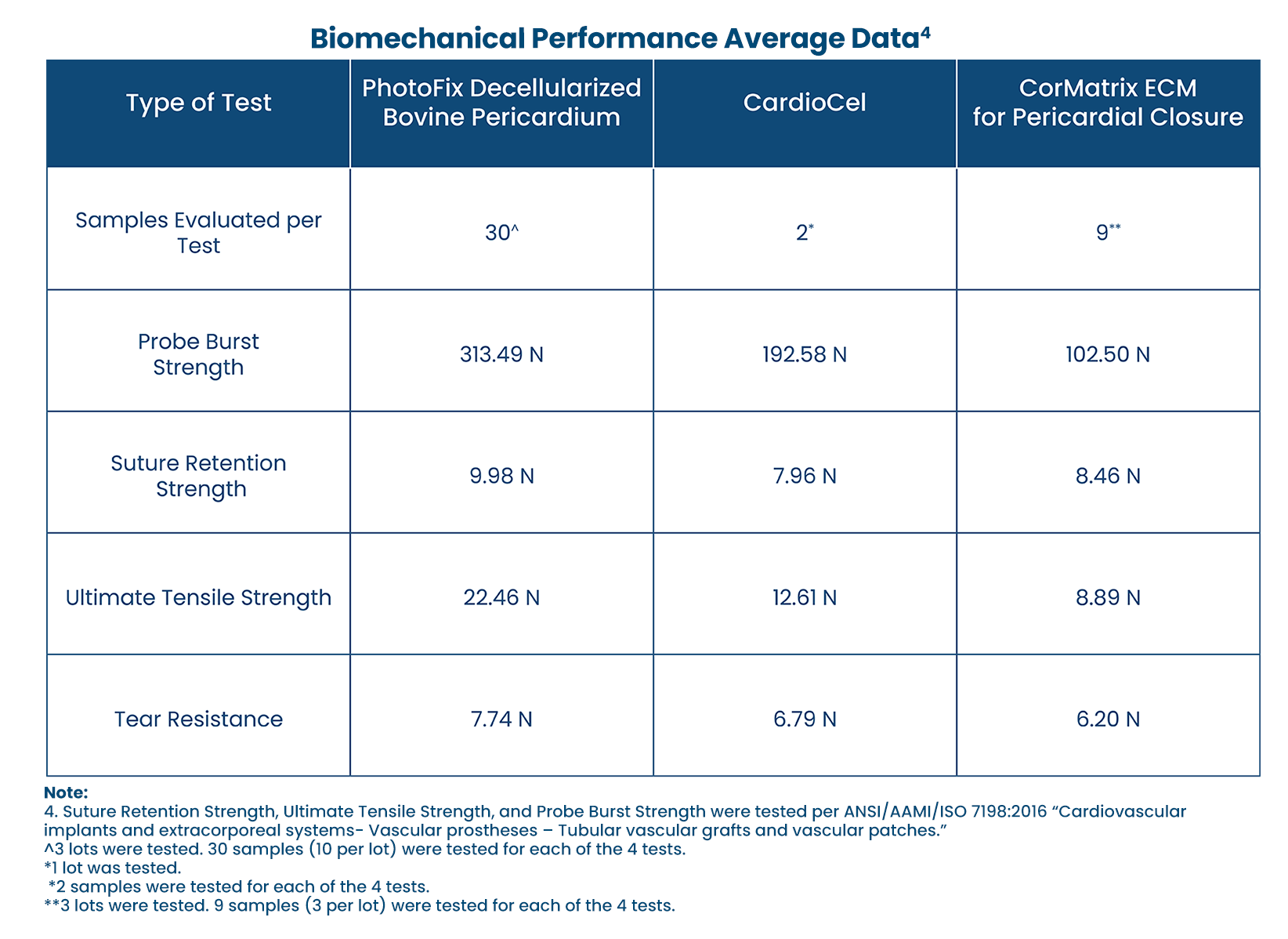
STRUCTURAL STRENGTH:
-
Comparison of biomechanical performance patches.
Additional Resources
Explore additional resources for PhotoFix below. For further information or to contact a sales associate in your area, contact us.
Product Highlights
- Artivion, Inc. Data on file.
- Schmidt C E, et. al. (2000). Acellular vascular tissues: Natural biomaterials for tissue repair and tissue engineering. Biomaterials, 21(22), 2215-2231.
Product Overview
- Schoen, F J, et. al. (2005). Calcification of tissue heart valve substitutes: progress toward understanding and prevention. Ann Thorac Surg, 79(3), 1072-1080.
- Umashankar P R, et. al. (2012). Glutaraldehyde treatment elicits toxic response compared to decellularization in bovine pericardium. Toxicol Int, 19(1), 51-58.
- Golomb G, et. al. (1987). The role of glutaraldehyde-induced cross-links in calcification of bovine pericardium used in cardiac valve bioprostheses. Am J Pathol, 127(1), 122-130.
- Moore M A, et. al. (2001). Calcification resistance, biostability, and low immunogenic potential of porcine heart valves modified by dye-mediated photooxidation. J Biomed Mater Res, 56(1), 24-30.
Clinical Evidence
- Baird C, et. al. (2016). Photo-oxidized bovine pericardium in congenital cardiac surgery: single-centre experience. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 24(2), 240-244.
- Artivion, Inc. Pre-Clinical Data on File.
- Schmidt C E, et. al. (2000). Acellular vascular tissues: Natural biomaterials for tissue repair and tissue engineering. Biomaterials, 21(22), 2215-2231.
- Artivion, Inc. Data on file.
All products and indications are not available/approved in all markets. All trademarks are owned by Artivion, Inc. or its subsidiaries. On-X Life Technologies, Inc., Jotec GmbH, and Ascyrus Medical GmbH are wholly owned subsidiaries of Artivion, Inc. MLENG1605.002 (2023-10)
| Artivion, Inc., 1655 Roberts Blvd NW, Kennesaw, GA 30144, US |

